PDL1V | PD-L1-directed Antibody Drug Conjugate
PF-08046054 is an investigational compound. Its safety and efficacy have not been established
Overview + Rationale
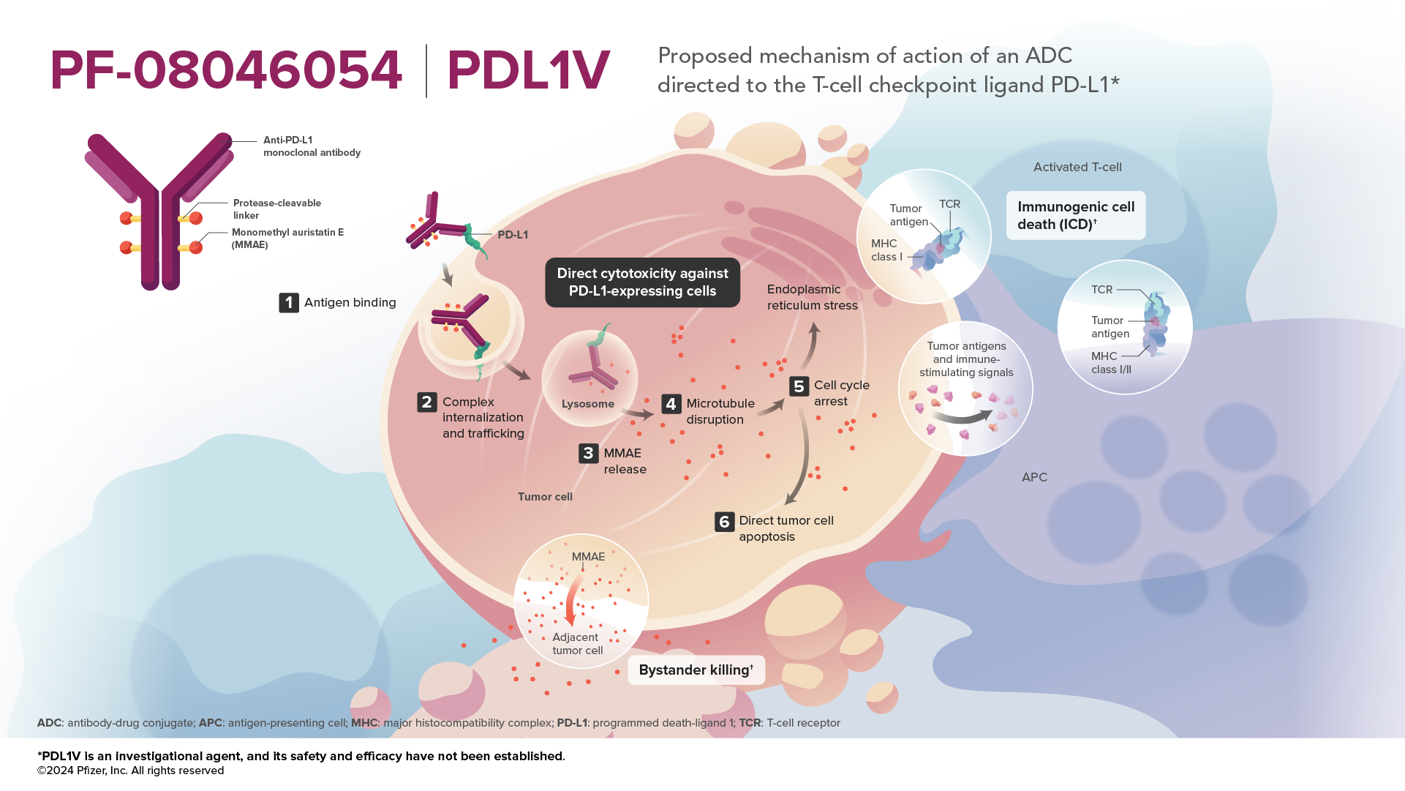
- PDL1V (PF-08046054) is a PD-L1-directed vedotin antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) that consists of a microtubule-disrupting agent (monomethyl auristatin E [MMAE]) connected to an anti-PD-L1 antibody by a protease-cleavable mc-vc linker.1
- PD-L1 functions as an immune checkpoint protein across many solid tumor types.
- PD-L1 expression on cancer cells facilitates tumor growth and immune evasion by suppressing T cells in the tumor microenvironment.1
- PD-L1 expression is elevated in multiple solid tumors, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, non-small-cell lung cancer, melanoma, triple-negative breast cancer, urothelial cancer, cervical cancer, gastric cancer, ovarian cancer, and esophageal cancer2-17
- The elevated expression of PD-L1 in solid tumors relative to normal tissue makes it an ideal molecular target for ADCs2
- The primary MOA of PDL1V is induction of tumor cell death through direct cytotoxicity via MMAE delivery to PD-L1 expressing cancer cells, bystander effect, and immunogenic cell death (ICD).1
- The PDL1V antibody has been designed to enable targeting of PD-L1 with an ADC through engineering for potential of increased internalization and payload delivery2
- While PDL1V targets PD-L1, pharmacokinetic data suggests traditional checkpoint inhibition through blockade of PD-(L)1 interactions is unlikely2
Mechanism of Action
Stage of Development
Advanced Solid Tumors
Thoracic Cancer & Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN)
Phase 3 Monotherapy

 Back
Back
